Breaking dam with Fluent2D and Abaqus2D
This example simulates a dam-break on a top-fixed flexible gate. The liquid, initially located in a free-surface tank, imposes a variable pressure on the bending flexible gate. This case has been examined numerically and experimentally by Antoci et al. [1]. Here, this 2D FSI calculation is performed with Fluent and Abaqus.
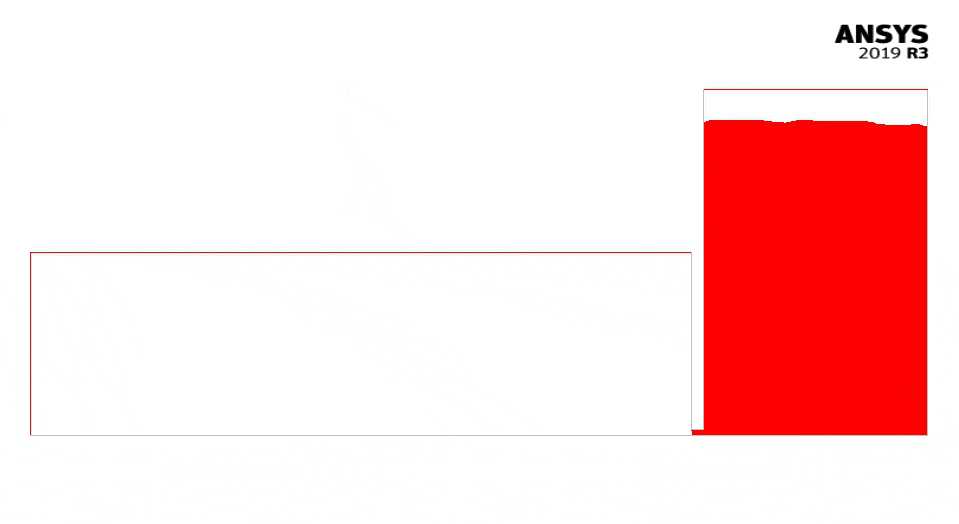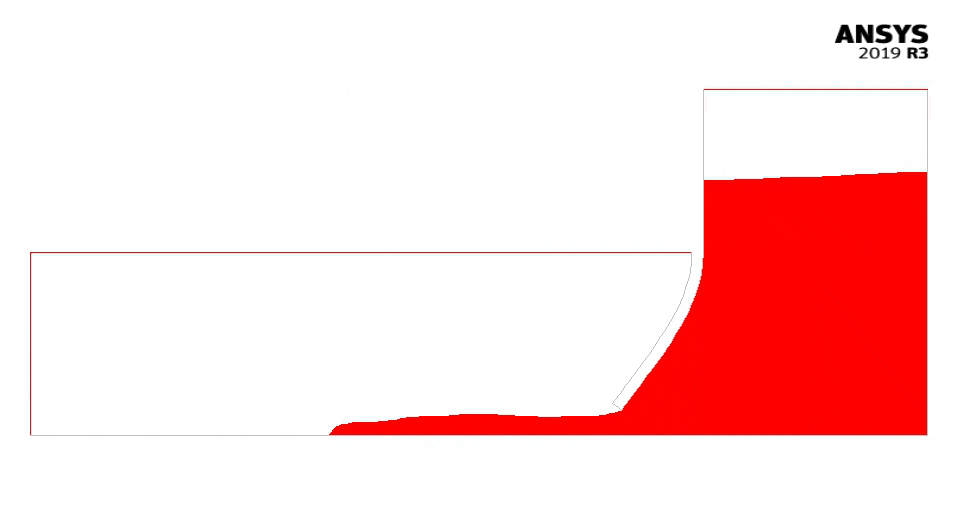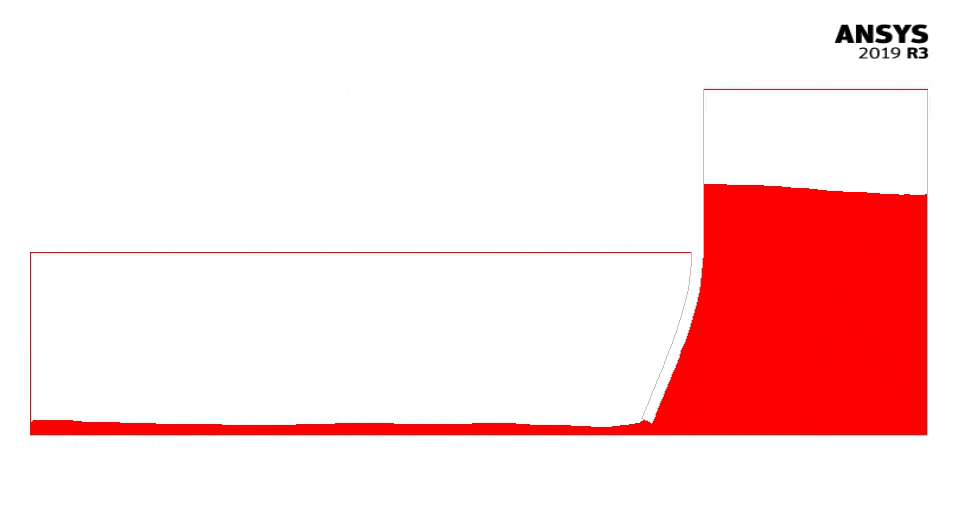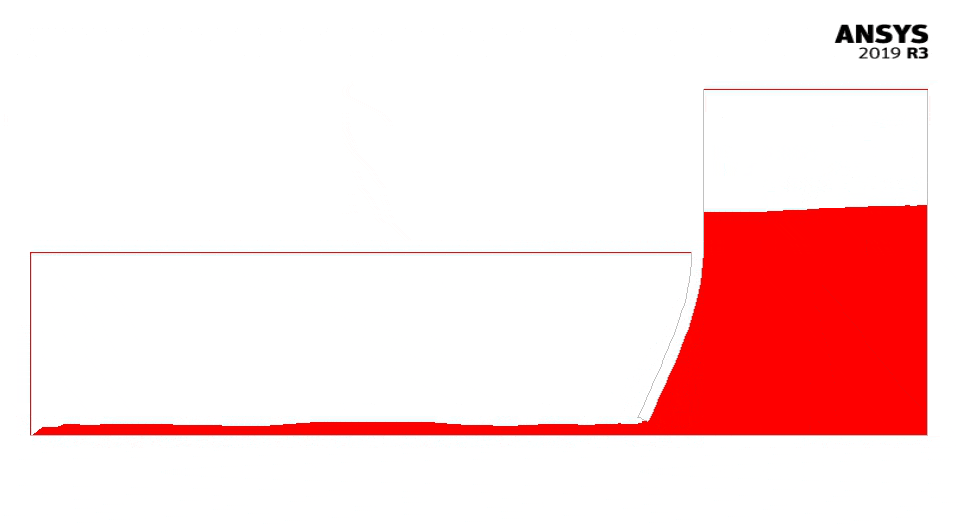
The figure below shows the bending of the gate and the flowing water (with Fluent).
The geometry is provided in the following figure. Pressure outlets and walls are indicated in blue and black, respectively.
The gap beneath the gate is exagerated for clarity.
The corresponding parameters are:
| parameter | value | description |
|---|---|---|
A |
0.1 m | Width of the liquid tank. |
G |
0.0025 m | Clearance of the elastic gate. |
H |
0.14 m | Initial height of the liquid column. |
L |
0.079 m | Height of the elastic gate. |
S |
0.005 m | Thickness of the elastic gate. |
The elastic gate is made of rubber and has the following parameters:
- density: 1100 kg/m³
- modulus of elasticity: 10^7 Pa
- poisson's ratio: 0.49
The flow calculation uses the volume of fluid (VOF) method to model the free-surface. The liquid phase is water with the following properties:
- density: 1000 kg/m³
- dynamic viscosity: 0.001 Pa\cdots
The gas phase is air modelled with the following parameters:
- density: 1.225 kg/m³
- dynamic viscosity: 1.7894 10^{-5} Pa\cdots
The gravitational accelartion is 9.81 m/s². The total simulated time is 0.4 s in time steps of 0.001 s.
Coupling algorithm
The coupling technique used is the interface quasi-Newton algorithm with an approximation for the inverse of the Jacobian from a least-squares model (IQN-ILS).
The reuse parameter q is set to 10, which means that data from the last ten time steps will be used to stabilize and accelerate the convergence.
Predictor
The initial guess in every time step is done using the linear predictor.
Convergence criterion
Two convergence criteria have been specified:
- The number of iterations in every time step is larger than 20.
- The residual norm on the displacement is a factor 10^{-3} lower than the initial value.
When either criterion is satisfied the simulation stops.
Solvers
Fluent is used as flow solver. The provided mesh is triangular. When the gate bends remeshing is performed to perserve its quality. A script to regenerate it using Gambit is included. This script allows to change the resolution and geometrical parameters.
The structural solver is Abaqus.
The Abaqus case is built when setting up the case starting from the file mesh_breaking_dam.inp containing nodes and elements.
This is done by running Abaqus with the make_inp.py Python script to set all parameters, such as surface definitions, material parameters, boundary conditions and time step information.
The result of the setup is a completed input file case_breaking_dam.inp.
The Abaqus element type used is CPE8R.
To exchange information between the solvers on the fluid-structure interface, the use of mappers is required. In the structural solver wrapper, a linear interpolation mapper is used to interpolate in the x- and y-direction from and to the coupled solver.
References
[1] Antoci C., Gallatie M. and Sibilla S., "Numerical simulation of fluid-structure interaction by SPH", Computers & Structures, vol. 85, no. 11, pp. 879-890, 2007.